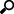Step 6: Name Your Application
|
|
|
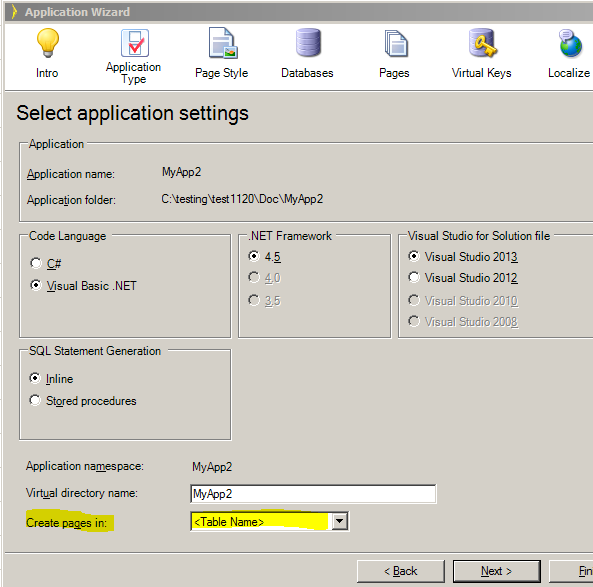
Use the Application Settings step to select your application’s name and type.(advanced view) |
The last step in creating a new application is to give it a name and location for its files. Additionally, you can choose the type of application to create and several other high-level options.
Related
Application Name and Folder Selection
Code Language and .NET Framework Selection
Visual Studio for Solution file
Namespace and Virtual Directory Selection
Application Name and Folder Selection
.NET Application Type
Your application can be structured internally in different ways, depending on how it is to be used.
Web Site for .NET
This option uses the folder-based structure defined for .NET Web applications, with its content defined by all files and folders under a root application folder. This organization makes explicit assumptions about the ~/App_Code, ~/App_Data, ~/App_GlobalResources, and ~/bin folders.
The Web Site is not compiled for deployment and pages are compiled dynamically at run-time when they are accessed using a .NET Just-In-Time (JIT) compiler. Iron Speed Designer also provides the option of pre-compiling a Web Site if it is targeted for deployment to a Microsoft IIS web server. Compilation uses the .NET Framework compilers (VBC/CSC) and is driven by the placement of code files in the application's special directories.
In the Web Site, external DLLs are included in the application by placing them in the \bin folder, where they are automatically referenced during compilation.
Web Application for .NET
This option organizes your application using the solution/project structure used by Visual Studio. Initially the solution (your application) contains three projects: the Main project, the Data Access Layer, and the Business Layer. The Web Application is compiled using Visual Studio and the compiled content is deployed to the web server. The Data Access and Business Layers are the implementation of the abstract layers described in the Iron Speed Designer Application Architecture document.
In Web Applications, compilation is controlled by the application project file, e.g.:
<AppName>.vbproj (.csproj)
Visual Studio is used for compilation and if not available, the .NET Framework compilers (VBC/CSC) are used.
External DLLs are included in the application by using Visual Studio to add a reference to the DLL in the project.
Additional references
Web Application Projects Overview:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa983474(VS.80).aspx
Shared Code Folders in ASP.NET Web Sites:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/t990ks23(VS.80).aspx
VS 2005 Web Deployment Projects:
http://weblogs.asp.net/scottgu/archive/2005/11/06/429723.aspx
VS 2008 Web Deployment Project Support Released:
Web Deployment Projects:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/magazine/cc163448.aspx
Web application project vs. web site:
http://vishaljoshi.blogspot.com/2009/08/web-application-project-vs-web-site.html
Code Language and .NET Framework Selection
Compilation and application building options govern how your application is compiled.
Code Language
Select the programming language for code created by Iron Speed Designer.
Note: You can change your application’s code language after it has been created. However, any modifications you make to the source code files will not be migrated to the updated application; you must port any code customizations by hand after switching code languages.
.NET Framework
Iron Speed Designer builds application targeting the following .NET Frameworks: 3.5, 4.0, 4.5. In some cases, the .NET Framework version you select automatically designates the compiler you must use to compile your application.
Note: Applications are not backward compatible. For example, once you have created an application using .NET Framework 4.5, you will not be able to switch to .NET Framework 4.0.
.NET Framework 4.0 caveats
The .NET Framework 4.0 Client Profile does not include these features:
-
ASP.NET
-
Advanced Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) functionality
-
.NET Framework Data Provider for Oracle
-
MSBuild for compiling
You must install the .NET Framework 4.0 to use these features in your application. The full .NET Framework 4.0 can be downloaded from:
Compiler
Microsoft Visual Studio .NET
Iron Speed Designer does not require you to use any particular integrated development environment, such as Microsoft Visual Studio .NET.
Asp .NET Development Server
Iron Speed Designer can run your application using either ASP.NET Development Server or the Microsoft Internet Information Server (IIS). ASP.NET Development Server is used as a a generic term in Iron Speed Desiner, referring to the original ASP.NET Development Server, called Cassini, or to its replacement IIS Express in Framework 4.5.
Visual Studio for Solution file
Select the Visual Studio version for which the application will be created. The solution/project files for your application will be generated based on the version of Visual Studio selected. Compilation and generation of deployment will take place using the selected Visual Studio. The capabilities of the Visual Studio will apply to the application. For instance, creating a Framework 4.0 application using Visual Studio 2012 will not allow MSI installer creation, using publishing in Visual Studio for deployment instead. The following table shows the .Net Framework and Visual Studio combinations allowed.
|
Application Type |
Framework |
Visual Studio |
|
Website/Web Application |
2008, 2010 |
|
|
Website/Web Application |
2010, 2012, 2013 |
|
|
Website/Web Application |
4.5 |
2012, 2013 |
|
SharePoint 2007 |
3.5 |
2008 |
|
SharePoint 2010 |
3.5 |
2008 |
SQL Statement Generation
Specifies where and how to create your application’s SQL. Iron Speed Designer automatically creates all the SQL statements required for each database-connected form, web page, table, and report in your application, as well as all the database access logic and storage management code. You do not need to know any SQL to build applications in Iron Speed Designer. The SQL is based on your database schema and user interface design. A variety of data filters and navigation components provide your application users with additional viewing and reporting flexibility.
Can’t create stored procedures in all cases
Iron Speed Designer may not be able to create stored procedures in all cases, even though you have selected this option. In these cases, Iron Speed Designer will create inline SQL. For example, Iron Speed Designer cannot create stored procedures for Microsoft Access databases, a database product which does not support stored procedures. Also, Iron Speed Designer will not create stored procedures in cases where it detects your database access credentials do not have sufficient permissions to load stored procedures into the database or execute them once there.
Other reasons why Iron Speed Designer can’t create stored procedures include:
-
Your database is “read only”. Check your database permissions to see if any setting has changed to make it read-only, which means stored procedures will not be created.
-
Your database tables or views are missing primary keys or Virtual Primary Keys. Check if the changes made to your database views render them capable of having stored procedures created. For example, a view without a Virtual Primary Key cannot have an Update stored procedure created.
-
The Stored Procedures option is set to 'true' in the <App Name>.config file.
<add key="GenerateStoredProcedures" value="True" />
Stored procedure owner
Iron Speed Designer creates stored procedures using the user name you provide to log into the database. We recommend you select the final user name you want to use in production. For example, this is frequently ‘dbo’ for Microsoft SQL Server databases.
Optimistic Concurrency Support
Iron Speed Designer generates dynamic SQL and Stored procedures to supports optimistic concurrency. I.e. if record has been changed after it was opened in the browser data access layer will prevent it from saving and give the application user a warning. You can override this behavior for dynamic SQL and force Data Access layer to save record without checking by setting SupportConcurrency key to False in the web.config.
Namespace and Virtual Directory Selection
Page Location